Flipping Your Classroom

Flipping the classroom, generally speaking, involves the use of a blended learning teaching model, where technology is used to provide students with the learning material outside of class, so that classroom time can be spent on interactive exercises and activities. Some phrase this as “lecture at home, practice at school.”
Ways to Flip Your Classroom
- Students read material, watch screencasts/multimedia, and take basic knowledge quizzes outside of class
- Class time is used for review, Q & A sessions, discussions, presentations, and hands-on practice time; can focus class time on games, experiments, performance arts, etc…
- Students can teach each other by making their own videos and posting documents and comments online and/or in the classroom
- Quiz students before class time to determine baseline knowledge and problem areas
- Students can take the same quiz before and then after clas to measure improved learning
- Consider using groups and/or learning/topics stations in the classroom
Advantages of Flipping
- Students can review the instruction repeatedly and at their own pace
- The flipped format can provide students with more control over their learning (where and how they learn)
- During practice in class, students can refer back to recordings and other content material before asking for one-on-one help
- Students that have excused absences from class due to illness, bad weather, etc… can stay on track
- Instructors can use the same content in multiple classes, over multiple semesters
- Provides students more time for mastery of the course material
For further information, you can check out:
- Educause’s “7 Things You Should Know About Flipped Classrooms.”
- The Official Peer Instruction Blog‘s Seven Myths about the Flipped Classroom
One Example of a Flipped Structure
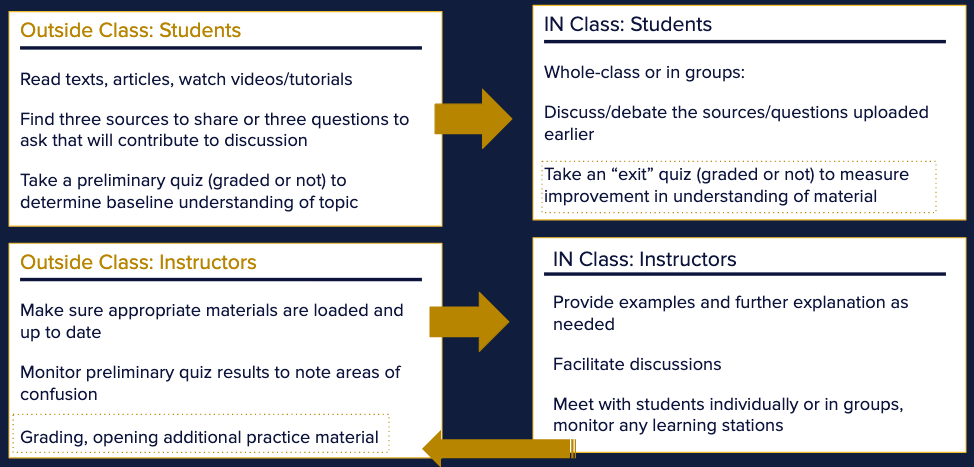
In the example above, students do all of their reading and multimedia activities outside of the classroom. They also do a basic assignment, such as find three articles to share with the class or compose three questions to share with the class. This can be posted in advance on a discussion board. Students are also expected to take a preliminary quiz to determine understanding of the topic. Outside of class, instructors must make sure that the necessary materials are loaded and up to date, and also monitor the quiz results to note concepts that need further explanation.
In the classroom, students, either as a whole-class or individually, discuss/debate the sources or questions uploaded earlier. Then they take an “exit” quiz to measure improvement in learning (this quiz can be taken in class or outside of class). In class, the instructor provides examples and further explanation of the material as needed and also facilitates the discussions. As appropriate, the instructor can also meet with students individually or in groups, monitoring any learning stations. Finally, the instructor does any outstanding grading and opens additional practice material as needed.
Cautions
- To work well, students must come to class prepared. This can lead to some student resistance, as they must do their assignments consistently in order to engage in the material in front of their peers. Consider allowing students one “free” day, where they don’t have to actively participate in the in-class activities?
- The online materials must be thorough, manageable, and understandable since students will likely be on their own for their first contact with the content.
- Consistency is key- students should be comfortable with what to expect (and what is expected of them) from class to class.
- Bias is a possible issue in some flipped classrooms- for maximum achievement, students must have regular and reliable access to the online material. In addition, students must also feel comfortable actively participating in class (self-confidence).
- It can be difficult to broadly evaluate the effectiveness of the flipped classroom concept because every flipped course can be different.
Resources
For Content:
- University Libraries: ebooks, streaming media, eReserves, Open Educational Resources (OER), Zotero for citations
- Khan Academy
- Canvas Studio for video: can do webcam video and screen recording (screencasting)
- The University Teaching & Learning Commons can record more professional video and/or provide a lightboard
- Programs such as Google Docs and Scrible allow document markup
For Activities and Assignments:
- Canvas Studio: allows video comments and embedded quizzes in video
- Canvas Groups
- Canvas Collaborations
- Canvas Quizzes, Discussions, and Assignments
As always, if choosing publisher material, make sure to confirm with your publisher rep that the content you select is accessible for all students.





